Mapping of the ISO/OSI model layers to their Azure equivalents:
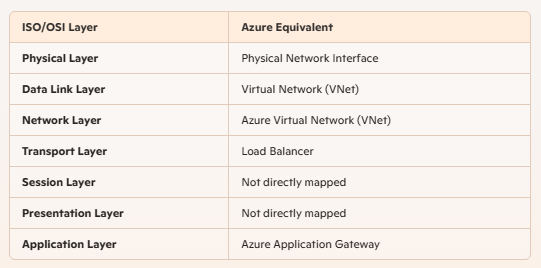
| ISO/OSI Layer | Azure Equivalent |
| Physical Layer | Physical Network Interface |
| Data Link Layer | Virtual Network (VNet) |
| Network Layer | Azure Virtual Network (VNet) |
| Transport Layer | Load Balancer |
| Session Layer | Not directly mapped |
| Presentation Layer | Not directly mapped |
| Application Layer | Azure Application Gateway |
- Physical Layer: This layer deals with the physical components of the network, such as cables, switches, and network interface cards (NICs). In Azure, this corresponds to the physical network interface that connects your virtual machines to the network.
- Data Link Layer: This layer is responsible for node-to-node data transfer and error detection/correction. In Azure, this is represented by the Virtual Network (VNet), which provides the underlying network infrastructure for your resources.
- Network Layer: This layer handles packet forwarding including routing through different routers. In Azure, this is represented by the Azure Virtual Network (VNet), which allows you to create isolated networks in the cloud.
- Transport Layer: This layer provides end-to-end communication services for applications. In Azure, this is represented by Load Balancers, which distribute traffic across multiple servers to ensure high availability and reliability.
- Session Layer: This layer manages sessions between applications. Azure does not have a direct equivalent for this layer, as session management is typically handled by the application layer.
- Presentation Layer: This layer translates data between the application layer and the network. Azure does not have a direct equivalent for this layer, as data translation is typically handled by the application layer.
- Application Layer: This layer provides network services to end-user applications. In Azure, this is represented by the Azure Application Gateway, which provides application-level routing and security.
